WIH International Hospital
Endoscopic Discectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation
Endoscopic Surgery for Herniated Discs: An Overview
Introduction
Endoscopic surgery for herniated discs is a minimally invasive procedure designed to relieve pain and neurological symptoms caused by herniated discs pressing on spinal nerves. This advanced technique utilizes a small camera to guide the surgeon in treating spinal conditions, offering several benefits over traditional open surgery.
What is Endoscopic Surgery for Herniated Discs?
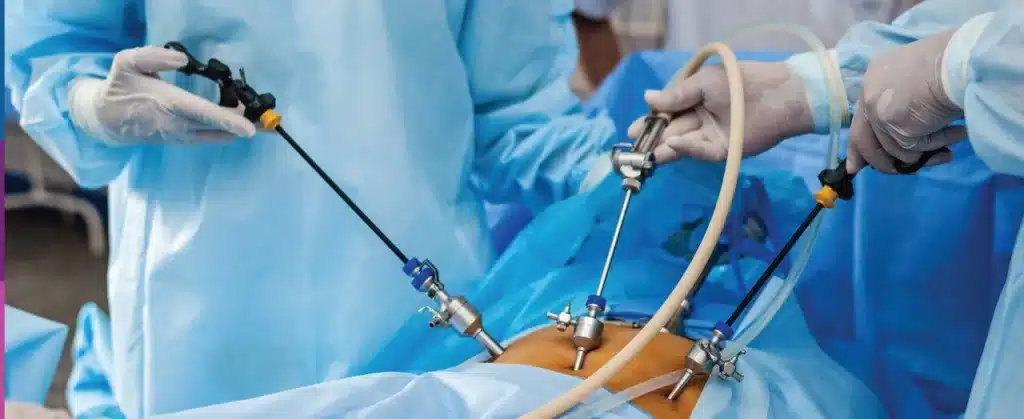
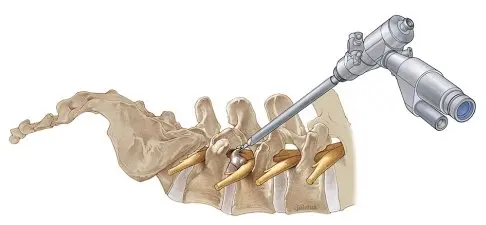
Endoscopic surgery involves the insertion of a small camera (endoscope) into the spinal region to visualize and address herniated discs. The procedure aims to alleviate severe back pain, leg pain (sciatica), and neurological deficits such as weakness or numbness in the legs.
Benefits of Endoscopic Surgery
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions lead to less tissue damage.
- Reduced Pain: Patients often experience less postoperative pain compared to traditional methods.
- Faster Recovery: Many patients return to normal activities more quickly, usually within 1-2 weeks.
Surgical Procedure Steps
- Anesthesia: The patient receives general anesthesia for comfort.
- Incision: A small incision is made in the skin over the spine.
- Insertion of Endoscope: The endoscope is carefully inserted into the spinal canal.
- Removal of Herniated Disc Material: Specialized instruments are used through the endoscope to remove the herniated portion of the disc.
- Closure: The incision is closed using sutures or adhesive strips.
Indications for Endoscopic Surgery
Endoscopic surgery is recommended for patients experiencing:
- Severe back pain radiating down the legs
- Muscle weakness or paralysis in the legs
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the lower extremities
- Chronic leg pain lasting more than six weeks
Possible Side Effects
While endoscopic surgery is generally safe, potential side effects may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve injury
- Persistent back pain
Recovery Timeline
Most patients are able to return home on the same day or the following day after surgery. Walking is encouraged within 1-2 days, and patients can typically resume normal activities within 1-2 weeks.
Postoperative Care Instructions
- Medication: Follow the prescribed medication regimen, including pain relief.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities initially.
- Gradual Resumption of Activities: Slowly increase activity levels as tolerated.
Frequently Asked Questions
What to Expect After Surgery
- Patients will wake up with various monitoring devices, including IV lines and vital signs monitors.
- Immediate neurological evaluations will be conducted.
- Patients may be transferred to a recovery room for monitoring.
When Can I Walk Again?
- Most patients are encouraged to start standing and walking by the second or third day post-surgery.
When Can the Surgical Site Get Wet?
- Surgical sites can typically be exposed to water once fully healed, usually within 10-14 days.
Why Do Some Patients Experience Delayed Healing?
- Healing times can vary based on wound size, depth, and patient factors such as age and nutrition.
Is Suture Removal Necessary?
- This depends on the type of sutures used; some dissolve while others require removal within 10-14 days.
When Should I Schedule My First Follow-Up?
- Generally, a follow-up appointment is scheduled for 7-10 days post-discharge.
What Symptoms Indicate Complications?
- Unusual pain, swelling, redness, discharge, or fever warrant immediate medical attention.
How Long Should I Wear a Back Brace?
- Depending on the type of surgery, braces may be recommended for 1-2 months.
When Can I Return to Work?
- Recovery times vary; many patients return to work within 2-3 weeks, while others may take 4-8 weeks.
What Activities Are Permissible Post-Surgery?
- Week 1: Short walks; avoid sitting for more than 20 minutes; follow medication and care instructions.
- Week 2: Increased daily activities; light lifting (up to 2 kg).
- Week 3: Longer walks; light household chores; lifting up to 5 kg.
- Week 4: Resuming normal activities and light exercise.
Conclusion
Endoscopic surgery for herniated discs offers a safe and effective solution for those suffering from debilitating back and leg pain. With its minimal invasiveness and quicker recovery time, it presents a viable option for many patients. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for your specific condition.