WIH International Hospital
Hip Arthroplasty
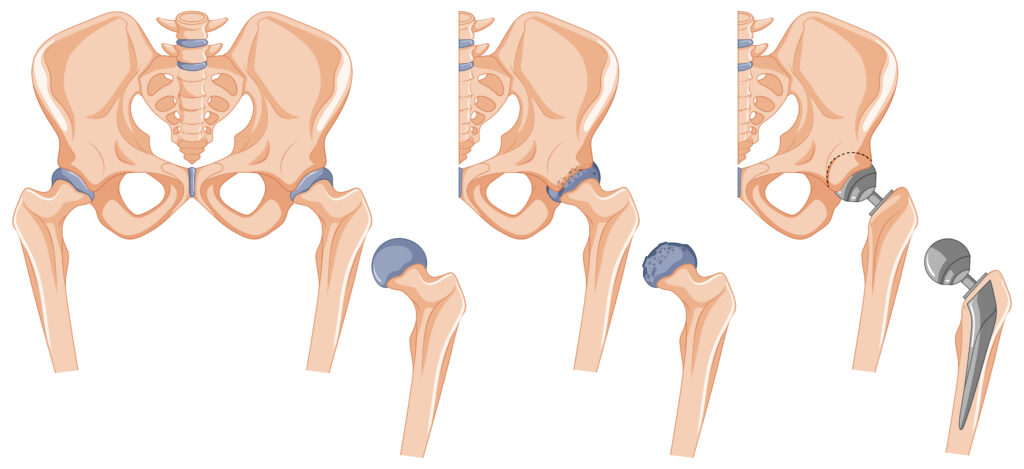
Hip arthroplasty, also known as hip replacement surgery, is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged or diseased hip joint with an artificial implant. This procedure is typically performed to relieve pain and improve mobility in individuals with conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and hip fractures.
Indications for Hip Arthroplasty
Hip arthroplasty is commonly considered for individuals who have:
-
Severe hip pain: Persistent pain in the hip joint that significantly interferes with daily activities and quality of life.
-
Limited hip mobility: Restricted range of motion in the hip, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or getting dressed.
-
Failed conservative treatments: Prior attempts to manage pain and improve function through non-surgical measures, such as physical therapy, pain medications, and lifestyle modifications, have been unsuccessful.
Types of Hip Arthroplasty
There are two main types of hip arthroplasty:
-
Total hip arthroplasty (THA): This procedure replaces both the ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) of the hip joint with artificial components.
-
Surface hip arthroplasty (resurfacing): This procedure involves replacing only the damaged surfaces of the hip joint, leaving the underlying bone intact. This type of arthroplasty is less common than THA and is typically reserved for younger patients with certain conditions.
Materials Used in Hip Implants
Hip implants are typically made from a combination of metals, such as titanium and cobalt-chromium, which are designed to be durable and biocompatible. The specific materials used may vary depending on the type of implant and the individual patient’s needs.
Benefits of Hip Arthroplasty
Hip arthroplasty can provide significant benefits for individuals with hip pain and mobility limitations, including :
-
Pain relief: The procedure can effectively alleviate pain and stiffness in the hip joint.
-
Improved mobility: Hip arthroplasty can restore range of motion and enable individuals to participate in daily activities more easily.
-
Enhanced quality of life: The surgery can significantly improve an individual’s overall quality of life by allowing them to engage in activities they may have previously avoided due to pain and limitations.
Risks and Complications
While hip arthroplasty is a generally safe and effective procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with the surgery, such as:
-
Infection: The risk of infection is relatively low but can have serious consequences.
-
Blood clots: Blood clots can form in the legs after surgery and may travel to other parts of the body, causing potentially life-threatening complications.
-
Implant loosening: Over time, the implant may loosen or dislocate, requiring revision surgery.
-
Nerve damage: Nerve damage can occur during the surgery, but the risk is low.
-
Leg length discrepancy: The surgery may result in a slight difference in leg length, which can be addressed with shoe lifts or other adjustments.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
After hip arthroplasty, most patients stay in the hospital for a few days and then undergo physical therapy to regain strength and mobility in the hip joint. The recovery process typically takes several weeks to months, and most individuals can return to their normal activities within 4-6 months.
Conclusion
Hip arthroplasty is a highly successful procedure that can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with hip pain and limited mobility. With careful patient selection, proper surgical technique, and comprehensive rehabilitation, hip arthroplasty can provide long-lasting relief and restore function to the hip joint.